Server Is Extremely Busy Give Us 10 Seconds and Try Again
This browser is no longer supported.
Upgrade to Microsoft Border to accept advantage of the latest features, security updates, and technical support.
Troubleshooting connectivity issues and other errors with Azure SQL Database and Azure SQL Managed Instance
APPLIES TO:  Azure SQL Database
Azure SQL Database  Azure SQL Managed Example
Azure SQL Managed Example
You receive error messages when the connection to Azure SQL Database or Azure SQL Managed Instance fails. These connection bug tin can be acquired by reconfiguration, firewall settings, a connection timeout, incorrect login information, or failure to apply all-time practices and design guidelines during the application design process. Additionally, if the maximum limit on some Azure SQL Database or SQL Managed Example resources is reached, you can no longer connect.
Transient fault fault messages (40197, 40613 and others)
The Azure infrastructure has the ability to dynamically reconfigure servers when heavy workloads ascend in the SQL Database service. This dynamic behavior might cause your client programme to lose its connexion to the database or instance. This kind of error status is called a transient fault. Database reconfiguration events occur because of a planned event (for example, a software upgrade) or an unplanned event (for instance, a process crash, or load balancing). Most reconfiguration events are more often than not short-lived and should be completed in less than 60 seconds at most. Withal, these events can occasionally take longer to stop, such as when a large transaction causes a long-running recovery. The following table lists various transient errors that applications can receive when connecting to Azure SQL Database.
List of transient fault mistake codes
| Fault lawmaking | Severity | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 926 | 14 | Database 'replicatedmaster' cannot exist opened. It has been marked SUSPECT by recovery. See the SQL Server errorlog for more information. This error may exist logged on SQL Managed Case errorlog, for a short period of time, during the last phase of a reconfiguration, while the old primary is shutting down its log. |
| 4060 | 16 | Cannot open up database "%.*ls" requested by the login. The login failed. For more information, run into Errors 4000 to 4999 |
| 40197 | 17 | The service has encountered an error processing your request. Delight try again. Error code %d. You lot receive this error when the service is down due to software or hardware upgrades, hardware failures, or any other failover problems. The error code (%d) embedded within the message of error 40197 provides additional information about the kind of failure or failover that occurred. Some examples of the error codes are embedded inside the bulletin of mistake 40197 are 40020, 40143, 40166, and 40540. Reconnecting automatically connects you to a healthy copy of your database. Your awarding must catch error 40197, log the embedded error code (%d) within the bulletin for troubleshooting, and attempt reconnecting to SQL Database until the resources are available, and your connection is established again. For more information, see Transient errors. |
| 40501 | 20 | The service is currently busy. Retry the request subsequently 10 seconds. Incident ID: %ls. Code: %d. For more than information, run into: • Logical SQL server resource limits • DTU-based limits for unmarried databases • DTU-based limits for elastic pools • vCore-based limits for single databases • vCore-based limits for elastic pools • Azure SQL Managed Instance resource limits. |
| 40613 | 17 | Database '%.*ls' on server '%.*ls' is non currently available. Please retry the connection later. If the trouble persists, contact client support, and provide them the session tracing ID of '%.*ls'. This mistake may occur if in that location is already an existing dedicated administrator connexion (DAC) established to the database. For more than information, see Transient errors. |
| 49918 | 16 | Cannot process request. Not enough resources to process asking. The service is currently busy. Please retry the request later. For more data, see: |
| 49919 | 16 | Cannot procedure create or update request. Too many create or update operations in progress for subscription "%ld". The service is busy processing multiple create or update requests for your subscription or server. Requests are currently blocked for resource optimization. Query sys.dm_operation_status for pending operations. Wait until pending create or update requests are complete or delete one of your pending requests and retry your request afterward. For more information, see: |
| 49920 | 16 | Cannot procedure request. Too many operations in progress for subscription "%ld". The service is busy processing multiple requests for this subscription. Requests are currently blocked for resource optimization. Query sys.dm_operation_status for performance status. Wait until pending requests are complete or delete one of your pending requests and retry your request later. For more information, run into: |
| 4221 | 16 | Login to read-secondary failed due to long look on 'HADR_DATABASE_WAIT_FOR_TRANSITION_TO_VERSIONING'. The replica is non available for login considering row versions are missing for transactions that were in-flight when the replica was recycled. The issue can be resolved by rolling back or committing the active transactions on the principal replica. Occurrences of this condition can be minimized by avoiding long write transactions on the primary. |
| 615 | 21 | Could not observe database ID %d, name '%.*ls' . Error Code 615. This means in-memory enshroud is not in-sync with SQL server instance and lookups are retrieving stale database ID. SQL logins use in-retention cache to get the database proper noun to ID mapping. The enshroud should exist in sync with backend database and updated whenever attach and disassemble of database to/from the SQL server instance occurs. Try reconnecting to SQL Database until the resource are available, and the connectedness is established over again. For more information, see Transient errors. |
Steps to resolve transient connectivity problems
- Check the Microsoft Azure Service Dashboard for any known outages that occurred during the time during which the errors were reported by the application.
- Applications that connect to a cloud service such every bit Azure SQL Database should expect periodic reconfiguration events and implement retry logic to handle these errors instead of surfacing application errors to users.
- Every bit a database approaches its resources limits, information technology can seem to be a transient connectivity issue. See Resource limits.
- If connectivity problems continue, or if the duration for which your application encounters the error exceeds threescore seconds or if you see multiple occurrences of the error in a given twenty-four hour period, file an Azure support request by selecting Get Support on the Azure Back up site.
Implementing Retry Logic
It is strongly recommended that your client program has retry logic so that it could reestablish a connexion after giving the transient fault time to correct itself. We recommend that you lot delay for 5 seconds before your first retry. Retrying later a delay shorter than 5-seconds risks overwhelming the cloud service. For each subsequent retry the filibuster should grow exponentially, up to a maximum of lx seconds.
For code examples of retry logic, meet:
- Connect resiliently to SQL with ADO.NET
- Connect resiliently to SQL with PHP
For additional information on handling transient errors in your awarding review Troubleshooting transient connection errors to SQL Database
A word of the blocking period for clients that apply ADO.Internet is available in Connexion Pooling (ADO.Cyberspace).
The effect occurs if the application can't connect to the server.
To resolve this issue, try the steps (in the order presented) in the Steps to ready common connection issues section.
The server/example was non found or was not accessible (errors 26, xl, 10053)
Error 26: Mistake Locating server specified
Organization.Data.SqlClient.SqlException: A network-related or instance-specific mistake occurred while establishing a connection to SQL Server. The server was not constitute or was not accessible. Verify that the instance name is correct and that SQL Server is configured to allow remote connections.(provider: SQL Network Interfaces, error: 26 – Error Locating Server/Case Specified)
Error forty: Could not open a connection to the server
A network-related or instance-specific mistake occurred while establishing a connectedness to SQL Server. The server was not found or was not accessible. Verify that the example proper noun is correct and that SQL Server is configured to allow remote connections. (provider: Named Pipes Provider, fault: forty - Could non open up a connectedness to SQL Server)
Mistake 10053: A transport-level error has occurred when receiving results from the server
10053: A send-level error has occurred when receiving results from the server. (Provider: TCP Provider, error: 0 - An established connexion was aborted by the software in your host auto)
These problems occur if the application can't connect to the server.
To resolve these problems, try the steps (in the order presented) in the Steps to fix common connexion bug section.
Cannot connect to server due to firewall issues
Fault 40615: Cannot connect to < servername >
To resolve this issue, configure firewall settings on SQL Database through the Azure portal.
Error 5: Cannot connect to < servername >
To resolve this upshot, brand certain that port 1433 is open for outbound connections on all firewalls betwixt the client and the internet.
Unable to log in to the server (errors 18456, 40531)
Login failed for user '< User name >'
Login failed for user '<User name>'.This session has been assigned a tracing ID of '<Tracing ID>'. Provide this tracing ID to customer support when you demand help. (Microsoft SQL Server, Mistake: 18456)
To resolve this effect, contact your service administrator to provide you with a valid user name and password.
Typically, the service ambassador can utilise the following steps to add together the login credentials:
-
Log in to the server by using SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS).
-
Run the following SQL query in the
chiefdatabase to check whether the login proper name is disabled:SELECT name, is_disabled FROM sys.sql_logins; -
If the respective name is disabled, enable information technology by using the following statement:
Change LOGIN <User name> ENABLE; -
If the SQL login user name doesn't exist, edit and run the following SQL query to create a new SQL login:
CREATE LOGIN <SQL_login_name, sysname, login_name> WITH PASSWORD = '<password, sysname, Change_Password>'; GO -
In SSMS Object Explorer, expand Databases.
-
Select the database that you want to grant the user permission to.
-
Right-click Security, and then select New, User.
-
In the generated script with placeholders (sample shown below), replace template parameters past following the steps here and execute information technology:
CREATE USER [<user_name, sysname, user_name>] FOR LOGIN [<login_name, sysname, login_name>] WITH DEFAULT_SCHEMA = [<default_schema, sysname, dbo>]; Go -- Add user to the database owner office EXEC sp_addrolemember North'db_owner', N'<user_name, sysname, user_name>'; GOYou tin can also utilize
sp_addrolememberto map specific users to specific database roles.Note
In Azure SQL Database, consider the newer ALTER Office syntax for managing database role membership.
For more information, see Managing databases and logins in Azure SQL Database.
Connection timeout expired errors
Arrangement.Information.SqlClient.SqlException (0x80131904): Connexion Timeout Expired
Organization.Data.SqlClient.SqlException (0x80131904): Connectedness Timeout Expired. The timeout period elapsed while attempting to eat the pre-login handshake acknowledgement. This could be because the pre-login handshake failed or the server was unable to respond dorsum in time. The duration spent while attempting to connect to this server was - [Pre-Login] initialization=iii; handshake=29995;
System.Information.SqlClient.SqlException (0x80131904): Timeout expired
System.Data.SqlClient.SqlException (0x80131904): Timeout expired. The timeout period elapsed prior to completion of the operation or the server is not responding.
Organization.Data.Entity.Core.EntityException: The underlying provider failed on Open
Arrangement.Data.Entity.Core.EntityException: The underlying provider failed on Open up. -> System.Data.SqlClient.SqlException: Timeout expired. The timeout period elapsed prior to completion of the functioning or the server is non responding. -> Organization.ComponentModel.Win32Exception: The look operation timed out
Cannot connect to < server name >
Cannot connect to <server name>.Additional Data:Connection Timeout Expired. The timeout period elapsed during the postal service-login phase. The connection could take timed out while waiting for server to complete the login process and answer; Or it could take timed out while attempting to create multiple active connections. The duration spent while attempting to connect to this server was - [Pre-Login] initialization=231; handshake=983; [Login] initialization=0; authentication=0; [Post-Login] complete=13000; (Microsoft SQL Server, Fault: -ii) For assist, click: http://become.microsoft.com/fwlink?ProdName=Microsoft%20SQL%20Server&EvtSrc=MSSQLServer&EvtID=-2&LinkId=20476 The wait performance timed out
These exceptions tin can occur either because of connection or query issues. To confirm that this fault is caused past connectivity issues, encounter Confirm whether an error is caused by a connectivity upshot.
Connection timeouts occur because the application tin't connect to the server. To resolve this issue, try the steps (in the order presented) in the Steps to prepare common connection issues section.
Resource governance errors
Azure SQL Database uses a resource governance implementation based on Resources Governor to enforce resources limits. Learn more than about resources management in Azure SQL Database.
The almost common resource governance errors are listed beginning with details, followed past a table of resources governance error letters.
Fault 10928: Resources ID : 1. The request limit for the database is %d and has been reached.
The detailed fault message in this case reads: Resource ID : one. The request limit for the database is %d and has been reached. See 'http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=267637' for assistance.
This mistake message indicates that the worker limit for Azure SQL Database has been reached. A value will be present instead of the placeholder %d. This value indicates the worker limit for your database at the fourth dimension the limit was reached.
Note
The initial offering of Azure SQL Database supported only single threaded queries. At that time, the number of requests was always equivalent to the number of workers. Error message 10928 in Azure SQL Database contains the wording "The asking limit for the database is N and has been reached" for backwards compatibility purposes. The limit reached is actually the number of workers. If your max degree of parallelism (MAXDOP) setting is equal to zero or is greater than one, the number of workers may be much higher than the number of requests, and the limit may be reached much sooner than when MAXDOP is equal to one.
Learn more about Sessions, workers, and requests.
Connect with the Defended Admin Connection (DAC) if needed
If a live incident is ongoing where the worker limit has been approached or reached, you may receive Error 10928 when you lot connect using SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) or Azure Data Studio. One session can connect using the Diagnostic Connection for Database Administrators (DAC) even when the maximum worker threshold has been reached.
To plant a connection with the DAC from SSMS:
- From the menu, select File > New > Database Engine Query
- From the connection dialog box in the Server Proper name field, enter
admin:<fully_qualified_server_name>(this volition be something likeadmin:servername.database.windows.cyberspace). - Select Options >>
- Select the Connection Properties tab
- In the Connect to database: box, type the proper noun of your database
- Select Connect.
If you receive Error 40613, Database '%.*ls' on server '%.*ls' is not currently available. Please retry the connection afterward. If the trouble persists, contact customer support, and provide them the session tracing ID of '%.*ls', this may point that some other session is already continued to the DAC. Just one session may connect to the DAC for a single database or an elastic pool at a fourth dimension.
If y'all run into the error 'Failed to connect to server' later selecting Connect, the DAC session may still take been established successfully if you are using a version of SSMS prior to 18.9. Early versions of SSMS attempted to provide Intellisense for connections to the DAC. This failed, as the DAC supports merely a single worker and Intellisense requires a separate worker.
You lot cannot use a DAC connection with Object Explorer.
Review your max_worker_percent usage
To find resource consumption statistics for your database for fourteen days, query the sys.resource_stats organisation catalog view. The max_worker_percent cavalcade shows the pct of workers used relative to the worker limit for your database. Connect to the principal database on your logical server to query sys.resource_stats.
SELECT start_time, end_time, database_name, sku, avg_cpu_percent, max_worker_percent, max_session_percent FROM sys.resource_stats; You can too query resource consumption statistics from the last hour from the sys.dm_db_resource_stats dynamic direction view. Connect direct to your database to query sys.dm_db_resource_stats.
SELECT end_time, avg_cpu_percent, max_worker_percent, max_session_percent FROM sys.dm_db_resource_stats; Lower worker usage when possible
Blocking chains can cause a sudden surge in the number of workers in a database. A big book of concurrent parallel queries may cause a high number of workers. Increasing your max degree of parallelism (MAXDOP) or setting MAXDOP to zero can increase the number of agile workers.
Triage an incident with insufficient workers past post-obit these steps:
-
Investigate if blocking is occurring or if you tin identify a big book of concurrent workers. Run the following query to examine current requests and bank check for blocking when your database is returning Error 10928. Y'all may need to connect with the Dedicated Admin Connection (DAC) to execute the query.
SELECT r.session_id, r.request_id, r.blocking_session_id, r.start_time, r.status, r.command, DB_NAME(r.database_id) AS database_name, (SELECT COUNT(*) FROM sys.dm_os_tasks Every bit t WHERE t.session_id=r.session_id and t.request_id=r.request_id) AS worker_count, i.parameters, i.event_info AS input_buffer, r.last_wait_type, r.open_transaction_count, r.total_elapsed_time, r.cpu_time, r.logical_reads, r.writes, southward.login_time, south.login_name, southward.program_name, southward.host_name FROM sys.dm_exec_requests as r JOIN sys.dm_exec_sessions as south on r.session_id=south.session_id OUTER Utilise sys.dm_exec_input_buffer (r.session_id,r.request_id) As i WHERE due south.is_user_process=i; GO-
Look for rows with a
blocking_session_idto identify blocked sessions. Observe eachblocking_session_idin the list to make up one's mind if that session is as well blocked. This volition somewhen atomic number 82 you to the head blocker. Melody the head blocker query. -
To place a big volume of concurrent workers, review the number of requests overall and the
worker_countcolumn for each request.Worker_countis the number of workers at the time sampled and may change over fourth dimension equally the request is executed. Tune queries to reduce resource utilization if the cause of increased workers is concurrent queries that are running at their optimal degree of parallelism. For more information, run across Query Tuning/Hinting.
-
-
Evaluate the maximum degree of parallelism (MAXDOP) setting for the database.
Increase worker limits
If the database consistently reaches its limit despite addressing blocking, optimizing queries, and validating your MAXDOP setting, consider adding more resource to the database to increment the worker limit.
Discover resource limits for Azure SQL Database past service tier and compute size:
- Resource limits for single databases using the vCore purchasing model
- Resource limits for elastic pools using the vCore purchasing model
- Resource limits for single databases using the DTU purchasing model
- Resources limits for elastic pools using the DTU purchasing model
Learn more about Azure SQL Database resource governance of workers.
Error 10929: Resource ID: 1
10929: Resources ID: ane. The %s minimum guarantee is %d, maximum limit is %d and the electric current usage for the database is %d. Withal, the server is currently too busy to support requests greater than %d for this database. See http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=267637 for aid. Otherwise, please try again later.
Fault 40501: The service is currently busy
40501: The service is currently busy. Retry the request afterward x seconds. Incident ID: %ls. Code: %d.
This is an engine throttling error, an indication that resource limits are existence exceeded.
For more information well-nigh resource limits, run across Logical SQL server resource limits.
Error 40544: The database has reached its size quota
40544: The database has reached its size quota. Partition or delete information, drop indexes, or consult the documentation for possible resolutions. Incident ID: <ID>. Code: <code>.
This error occurs when the database has reached its size quota.
The following steps can either help you piece of work around the trouble or provide you with more options:
-
Cheque the electric current size of the database past using the dashboard in the Azure portal.
Note
To identify which tables are consuming the most space and are therefore potential candidates for cleanup, run the following SQL query:
SELECT o.name, SUM(p.row_count) AS 'Row Count', SUM(p.reserved_page_count) * viii.0 / 1024 As 'Tabular array Size (MB)' FROM sys.objects o Join sys.dm_db_partition_stats p on p.object_id = o.object_id Group By o.name ORDER Past [Table Size (MB)] DESC; GO -
If the current size does not exceed the maximum size supported for your edition, you can use ALTER DATABASE to increment the MAXSIZE setting.
-
If the database is already by the maximum supported size for your edition, endeavour one or more of the following steps:
- Perform normal database cleanup activities. For example, make clean up the unwanted information by using truncate/delete, or move information out past using SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) or the bulk copy plan (bcp) utility.
- Partitioning or delete data, drop indexes, or consult the documentation for possible resolutions.
- For database scaling, meet Scale single database resource and Scale elastic puddle resources.
Error 40549: Session is terminated because yous accept a long-running transaction
40549: Session is terminated because you have a long-running transaction. Try shortening your transaction.
If you repeatedly encounter this error, try to resolve the result by post-obit these steps:
-
Run the post-obit query to run into any open sessions that have a high value for the
duration_mscolumn:SELECT r.start_time, DATEDIFF(ms,start_time, SYSDATETIME()) as duration_ms, r.session_id, r.request_id, r.blocking_session_id, r.status, r.control, DB_NAME(r.database_id) AS database_name, i.parameters, i.event_info Equally input_buffer, r.last_wait_type, r.open_transaction_count, r.total_elapsed_time, r.cpu_time, r.logical_reads, r.writes, s.login_time, s.login_name, s.program_name, s.host_name FROM sys.dm_exec_requests as r Bring together sys.dm_exec_sessions as southward on r.session_id=southward.session_id OUTER Utilize sys.dm_exec_input_buffer (r.session_id,r.request_id) Every bit i WHERE south.is_user_process=1 ORDER BY start_time ASC; BecomeY'all may choose to ignore rows where the
input_buffercavalcade shows a query reading fromsys.fn_MSxe_read_event_stream: these requests are related to Extended Upshot sessions. -
Review the
blocking_session_idcolumn to encounter if blocking is contributing to long-running transactions. -
Consider batching your queries. For information on batching, come across How to use batching to improve SQL Database application performance.
Error 40551: The session has been terminated because of excessive TEMPDB usage
40551: The session has been terminated because of excessive TEMPDB usage. Try modifying your query to reduce the temporary tabular array space usage.
To work effectually this issue, follow these steps:
- Change the queries to reduce temporary table space usage.
- Drop temporary objects after they're no longer needed.
- Truncate tables or remove unused tables.
Error 40552: The session has been terminated because of excessive transaction log space usage
40552: The session has been terminated considering of excessive transaction log infinite usage. Try modifying fewer rows in a unmarried transaction.
To resolve this issue, try the post-obit methods:
-
The event can occur because of insert, update, or delete operations. Endeavour to reduce the number of rows that are operated on immediately by implementing batching or splitting into multiple smaller transactions.
-
The issue tin can occur because of index rebuild operations. To piece of work around this issue, brand sure the number of rows that are affected in the tabular array * (average size of field that'due south updated in bytes + 80) < 2 gigabytes (GB).
Note
For an alphabetize rebuild, the average size of the field that's updated should be substituted by the boilerplate alphabetize size.
Mistake 40553: The session has been terminated considering of excessive retentiveness usage
40553: The session has been terminated because of excessive memory usage. Try modifying your query to process fewer rows.
To work around this outcome, try to optimize the query.
For an in-depth troubleshooting procedure, meet Is my query running fine in the deject?.
For more data on other out of retentiveness errors and sample queries, see Troubleshoot out of retention errors with Azure SQL Database.
Table of resources governance fault messages
| Error code | Severity | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 10928 | 20 | Resources ID: %d. The %s limit for the database is %d and has been reached. Run across 'http://get.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=267637' for help.. The Resource ID indicates the resource that has reached the limit. When Resource ID = 1, this indicates a worker limit has been reached. Acquire more in Error 10928: Resource ID : ane. The asking limit for the database is %d and has been reached. When Resource ID = ii, this indicates the session limit has been reached. Learn more than nigh resource limits: |
| 10929 | xx | Resource ID: %d. The %southward minimum guarantee is %d, maximum limit is %d, and the current usage for the database is %d. However, the server is currently too busy to support requests greater than %d for this database. The Resource ID indicates the resource that has reached the limit. For worker threads, the Resources ID = i. For sessions, the Resources ID = two. For more information, encounter: • Logical SQL server resource limits • DTU-based limits for unmarried databases • DTU-based limits for elastic pools • vCore-based limits for single databases • vCore-based limits for elastic pools • Azure SQL Managed Instance resources limits. Otherwise, try once again afterwards. |
| 40544 | 20 | The database has reached its size quota. Partition or delete data, drop indexes, or consult the documentation for possible resolutions. For database scaling, run across Scale single database resources and Scale elastic pool resources. |
| 40549 | 16 | Session is terminated considering yous accept a long-running transaction. Try shortening your transaction. For data on batching, run across How to use batching to improve SQL Database application performance. |
| 40550 | sixteen | The session has been terminated considering it has acquired as well many locks. Try reading or modifying fewer rows in a single transaction. For information on batching, see How to use batching to improve SQL Database application performance. |
| 40551 | 16 | The session has been terminated because of excessive TEMPDB usage. Endeavour modifying your query to reduce the temporary tabular array infinite usage.If yous are using temporary objects, conserve space in the |
| 40552 | 16 | The session has been terminated because of excessive transaction log space usage. Try modifying fewer rows in a single transaction. For information on batching, see How to utilise batching to improve SQL Database application performance. If you perform majority inserts using the |
| 40553 | 16 | The session has been terminated because of excessive retention usage. Endeavor modifying your query to process fewer rows. Reducing the number of |
Elastic pool errors
The following errors are related to creating and using elastic pools:
| Error lawmaking | Severity | Description | Cosmetic action |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1132 | 17 | The rubberband pool has reached its storage limit. The storage usage for the rubberband pool cannot exceed (%d) MBs. Attempting to write data to a database when the storage limit of the elastic puddle has been reached. For information on resource limits, see: • DTU-based limits for elastic pools • vCore-based limits for elastic pools. | Consider increasing the DTUs of and/or calculation storage to the elastic pool if possible in order to increase its storage limit, reduce the storage used past private databases within the elastic pool, or remove databases from the rubberband pool. For elastic pool scaling, encounter Scale elastic puddle resources. For more information on removing unused space from databases, see Manage file space for databases in Azure SQL Database. |
| 10929 | 16 | The %s minimum guarantee is %d, maximum limit is %d, and the current usage for the database is %d. However, the server is currently as well busy to support requests greater than %d for this database. For information on resources limits, see: • DTU-based limits for elastic pools • vCore-based limits for elastic pools. Otherwise, endeavour again later. DTU / vCore min per database; DTU / vCore max per database. The total number of concurrent workers beyond all databases in the elastic pool attempted to exceed the pool limit. | Consider increasing the DTUs or vCores of the elastic pool if possible in order to increase its worker limit, or remove databases from the rubberband pool. |
| 40844 | 16 | Database '%ls' on Server '%ls' is a '%ls' edition database in an elastic pool and cannot have a continuous copy relationship. | N/A |
| 40857 | 16 | Elastic pool non constitute for server: '%ls', elastic pool name: '%ls'. Specified elastic pool does not exist in the specified server. | Provide a valid elastic pool name. |
| 40858 | 16 | Elastic puddle '%ls' already exists in server: '%ls'. Specified elastic puddle already exists in the specified server. | Provide new elastic pool proper name. |
| 40859 | xvi | Elastic pool does not back up service tier '%ls'. Specified service tier is not supported for rubberband pool provisioning. | Provide the correct edition or leave service tier blank to use the default service tier. |
| 40860 | 16 | Elastic pool '%ls' and service objective '%ls' combination is invalid. Elastic pool and service tier tin can be specified together only if resource type is specified as 'ElasticPool'. | Specify correct combination of elastic puddle and service tier. |
| 40861 | 16 | The database edition '%.*ls' cannot exist different than the elastic pool service tier which is '%.*ls'. The database edition is different than the rubberband puddle service tier. | Do not specify a database edition that is different than the elastic pool service tier. Note that the database edition does not demand to be specified. |
| 40862 | 16 | Elastic puddle name must exist specified if the rubberband pool service objective is specified. Elastic pool service objective does not uniquely identify an rubberband puddle. | Specify the elastic pool name if using the rubberband pool service objective. |
| 40864 | 16 | The DTUs for the rubberband pool must be at least (%d) DTUs for service tier '%.*ls'. Attempting to set the DTUs for the elastic pool below the minimum limit. | Retry setting the DTUs for the elastic pool to at least the minimum limit. |
| 40865 | xvi | The DTUs for the rubberband pool cannot exceed (%d) DTUs for service tier '%.*ls'. Attempting to set the DTUs for the elastic puddle above the maximum limit. | Retry setting the DTUs for the elastic pool to no greater than the maximum limit. |
| 40867 | 16 | The DTU max per database must exist at least (%d) for service tier '%.*ls'. Attempting to set the DTU max per database below the supported limit. | Consider using the elastic pool service tier that supports the desired setting. |
| 40868 | 16 | The DTU max per database cannot exceed (%d) for service tier '%.*ls'. Attempting to set the DTU max per database beyond the supported limit. | Consider using the elastic pool service tier that supports the desired setting. |
| 40870 | xvi | The DTU min per database cannot exceed (%d) for service tier '%.*ls'. Attempting to set the DTU min per database across the supported limit. | Consider using the elastic pool service tier that supports the desired setting. |
| 40873 | 16 | The number of databases (%d) and DTU min per database (%d) cannot exceed the DTUs of the rubberband pool (%d). Attempting to specify DTU min for databases in the elastic pool that exceeds the DTUs of the rubberband pool. | Consider increasing the DTUs of the elastic pool, or decrease the DTU min per database, or decrease the number of databases in the elastic pool. |
| 40877 | sixteen | An elastic pool cannot be deleted unless it does non contain any databases. The elastic pool contains 1 or more databases and therefore cannot be deleted. | Remove databases from the elastic puddle in order to delete it. |
| 40881 | 16 | The elastic pool '%.*ls' has reached its database count limit. The database count limit for the elastic pool cannot exceed (%d) for an elastic pool with (%d) DTUs. Attempting to create or add database to elastic pool when the database count limit of the elastic pool has been reached. | Consider increasing the DTUs of the rubberband pool if possible in lodge to increment its database limit, or remove databases from the elastic pool. |
| 40889 | xvi | The DTUs or storage limit for the elastic puddle '%.*ls' cannot be decreased since that would not provide sufficient storage infinite for its databases. Attempting to decrease the storage limit of the elastic pool below its storage usage. | Consider reducing the storage usage of individual databases in the elastic pool or remove databases from the pool in gild to reduce its DTUs or storage limit. |
| 40891 | 16 | The DTU min per database (%d) cannot exceed the DTU max per database (%d). Attempting to gear up the DTU min per database higher than the DTU max per database. | Ensure the DTU min per databases does not exceed the DTU max per database. |
| TBD | 16 | The storage size for an individual database in an elastic pool cannot exceed the max size allowed by '%.*ls' service tier rubberband pool. The max size for the database exceeds the max size allowed by the elastic puddle service tier. | Set the max size of the database within the limits of the max size allowed by the rubberband pool service tier. |
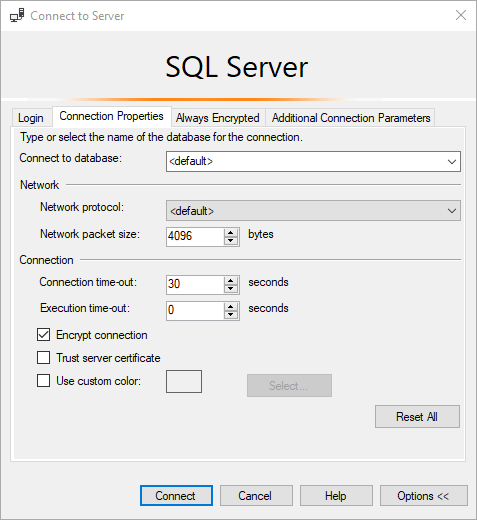
Cannot open database "chief" requested by the login. The login failed
This issue occurs considering the business relationship doesn't have permission to access the main database. Only by default, SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) tries to connect to the master database.
To resolve this result, follow these steps:
-
On the login screen of SSMS, select Options, and then select Connexion Properties.
-
In the Connect to database field, enter the user'due south default database proper name as the default login database, and and then select Connect.
Read-only errors
If you attempt to write to a database that is read-but, y'all'll receive an error. In some scenarios, the cause of the database's read-just status may not be immediately articulate.
Mistake 3906: Failed to update database "DatabaseName" considering the database is read-simply.
When attempting to modify a read-but database, the post-obit error will exist raised.
Msg 3906, Level 16, Land 2, Line 1 Failed to update database "%d" because the database is read-merely. You may be continued to a read-simply replica
For both Azure SQL Database and Azure SQL Managed Example, you may be continued to a database on a read-only replica. In this case, the post-obit query using the DATABASEPROPERTYEX() part will return READ_ONLY:
SELECT DATABASEPROPERTYEX(DB_NAME(), 'Updateability'); Get If y'all're connecting using SQL Server Direction Studio, verify if you have specified ApplicationIntent=ReadOnly in the Additional Connection Parameters tab on your connection options.
If the connection is from an application or a customer using a connection string, validate if the connection string has specified ApplicationIntent=ReadOnly. Learn more in Connect to a read-only replica.
The database may exist set to read-but
If y'all're using Azure SQL Database, the database itself may have been set up to read-only. Yous tin verify the database's status with the following query:
SELECT proper name, is_read_only FROM sys.databases WHERE database_id = DB_ID(); Y'all can change the read-merely condition for a database in Azure SQL Database using Alter DATABASE Transact-SQL. Yous tin't currently set up a database in a managed instance to read-simply.
Ostend whether an fault is caused by a connectivity upshot
To confirm whether an error is caused past a connectivity issue, review the stack trace for frames that show calls to open a connection like the following ones (annotation the reference to the SqlConnection grade):
System.Data.SqlClient.SqlConnection.TryOpen(TaskCompletionSource`i retry) at Arrangement.Information.SqlClient.SqlConnection.Open up() at AzureConnectionTest.Plan.Principal(String[] args) ClientConnectionId:<Customer connection ID> When the exception is triggered by query issues, you'll notice a call stack that'south similar to the following (note the reference to the SqlCommand grade). In this situation, tune your queries.
at Arrangement.Data.SqlClient.SqlCommand.ExecuteReader() at AzureConnectionTest.Program.Primary(String[] args) ClientConnectionId:<Customer ID> For additional guidance on fine-tuning performance, encounter the following resources:
- How to maintain Azure SQL indexes and statistics
- Manual tune query performance in Azure SQL Database
- Monitoring performance Azure SQL Database by using dynamic management views
- Operating the Query Store in Azure SQL Database
Steps to fix common connexion issues
-
Make sure that TCP/IP is enabled every bit a client protocol on the application server. For more data, see Configure client protocols. On application servers where you don't accept SQL tools installed, verify that TCP/IP is enabled by running cliconfg.exe (SQL Server Customer Network utility).
-
Check the awarding's connection cord to brand sure information technology'due south configured correctly. For case, make sure that the connection string specifies the correct port (1433) and fully qualified server name. See Get connectedness information.
-
Endeavor increasing the connection timeout value. Nosotros recommend using a connectedness timeout of at to the lowest degree thirty seconds.
-
Test the connectivity between the awarding server and the Azure SQL Database past using SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS), a UDL file, ping, or telnet. For more information, see Troubleshooting connectivity issues and Diagnostics for connectivity issues.
Note
As a troubleshooting stride, you tin can also exam connectivity on a different client computer.
-
As a all-time practise, make certain that the retry logic is in place. For more than information about retry logic, run into Troubleshoot transient faults and connection errors to SQL Database.
If these steps don't resolve your problem, effort to collect more data and then contact support. If your awarding is a cloud service, enable logging. This stride returns a UTC time stamp of the failure. Additionally, SQL Database returns the tracing ID. Microsoft Customer Support Services tin can use this information.
For more information about how to enable logging, meet Enable diagnostics logging for apps in Azure App Service.
Next steps
Learn more near related topics in the post-obit articles:
- Azure SQL Database connectivity compages
- Azure SQL Database and Azure Synapse Analytics network access controls
- Troubleshooting transaction log errors with Azure SQL Database and Azure SQL Managed Instance
- Troubleshoot transient connexion errors in SQL Database and SQL Managed Instance
- Analyze and prevent deadlocks in Azure SQL Database
Feedback
Submit and view feedback for
Source: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-sql/database/troubleshoot-common-errors-issues
0 Response to "Server Is Extremely Busy Give Us 10 Seconds and Try Again"
Post a Comment